2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019
All-Mechanical Resoswitch Receiver and Trigger Detector [2017]
Read More
The year 2017 brought about several landmark achievements. It advanced the practical utility of all-mechanical resoswitch communication devices, introducing the first squegging-based clock generator and the first functional all-mechanical zero-quiescent power trigger detector with no false positives. It delivered the first capacitive-gap transduced 60-MHz micromechanical resonator employing gaps down to 13-nm, making possible a (Cx/Co)-Q product of 480, which was astonishing at the time. Finally, this year achieved the first demonstration of ruthenium resonators that outperform polysilicon equivalents in Q, while using fabrication temperatures amenable to future integration directly over modern CMOS. 2017 was the launch point for intense research on gap-scaling and MEMS-CMOS integration to come.
R. Liu, J. N. Nilchi, and C. T.-C. Nguyen, “CW-powered squegging micromechanical clock generator,” Tech. Digest, 2017 IEEE Int. Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Conference, Las Vegas, Nevada, Jan. 22-26, 2017, pp. 905-908, DOI: 10.1109/MEMSYS.2017.7863555.
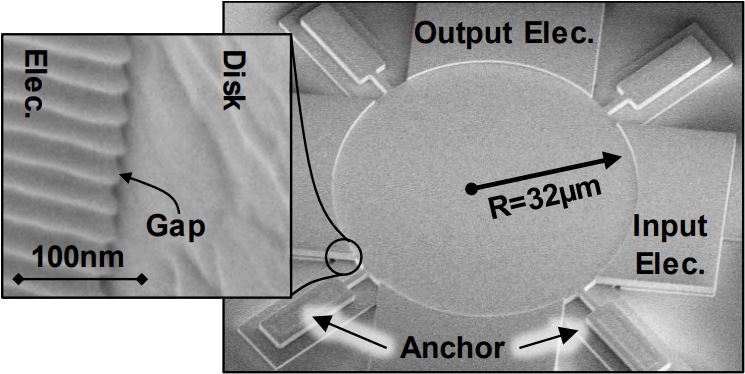
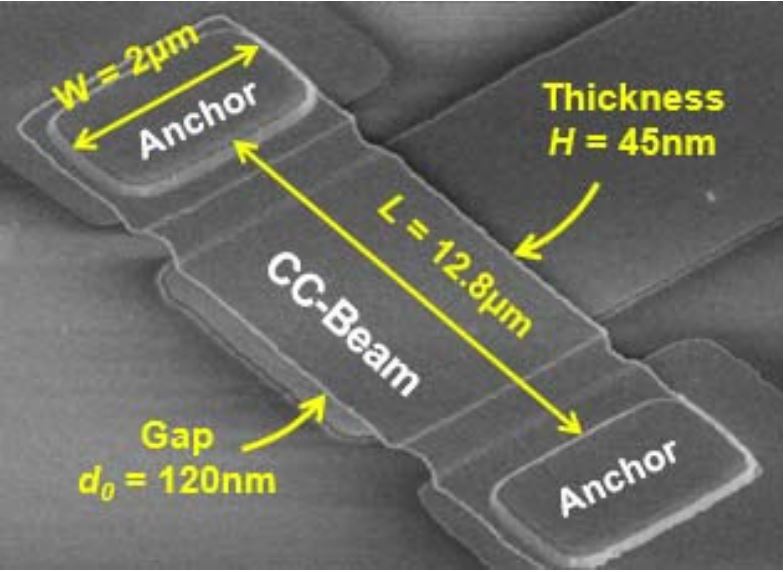
J. N. Nilchi, R. Liu, and C. T.-C. Nguyen, “High Cx/Co 13nm-capacitive-gap transduced disk resonator,” Tech. Digest, 2017 IEEE Int. Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Conference, Las Vegas, Nevada, Jan. 22-26, 2017, pp. 924-927, DOI: 10.1109/MEMSYS.2017.7863560.
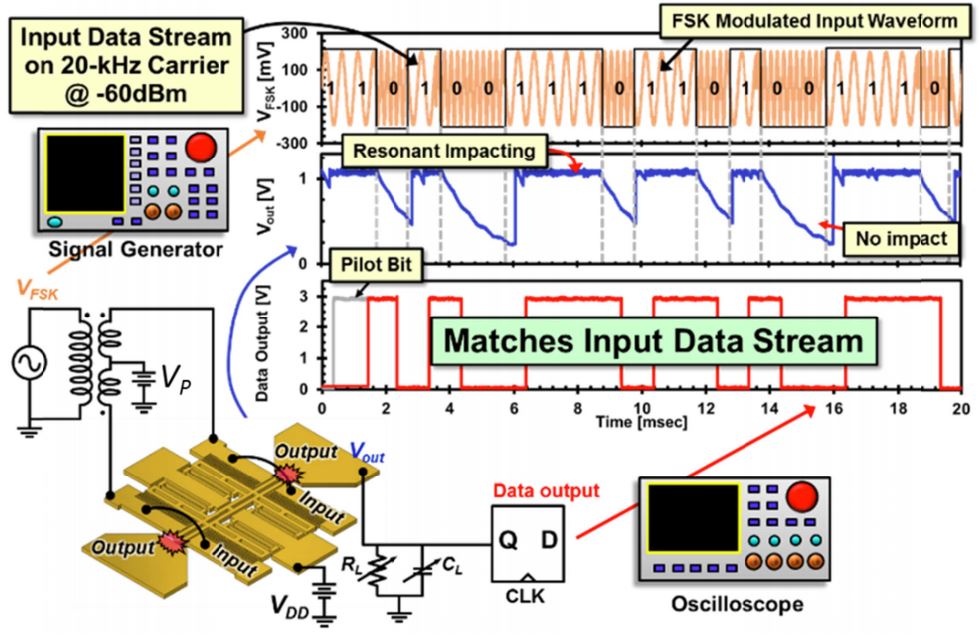
C. T.-C. Nguyen, R. Liu, and J. N. Nilchi, “An ultra-low power mechanical trigger detector (invited),” Proceedings, 2017 Gov. Microcircuit Applications & Critical Technology Conf., Reno, Nevada, March 20-23, 2017, pp. 104-107.
A. Ozgurluk, R. Liu, and C. T.-C. Nguyen, “Q-boosting of metal MEMS resonators via localized anneal-induced tensile stress,” Proceedings, IEEE Int. Frequency Control Symp., Besancon, France, July 10-13, 2017, pp. 10-15, DOI: 10.1109/FCS.2017.8088786.