Problem 1. (8 points) Program Errors and Java Keywords.
a. The variable i has not been declared. Add an int i; (as a separate line or in the for statement).
The run-time exception (an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException) arises when Java tries to access the invalid array member a[i - 1] with i equal to zero. Fix it by taking advantage of short-circuiting in the if statement:
if (i != 0 && a[i].length() > a[i - 1].length()) {
The debugged program prints out the command-line parameters,
appending a "9" to each parameter that is longer than
the previous parameter.
b. These three lines won't compile.
Object o = new Comparable();
double d = ((Object) "string").length();
int i = Integer.parseInt(super.toString());
You cannot construct a Comparable object,
because Comparable is a Java interface.
The class Object has no length method.
In a static method like main, there is no super.
c. static final.
d. continue and return.
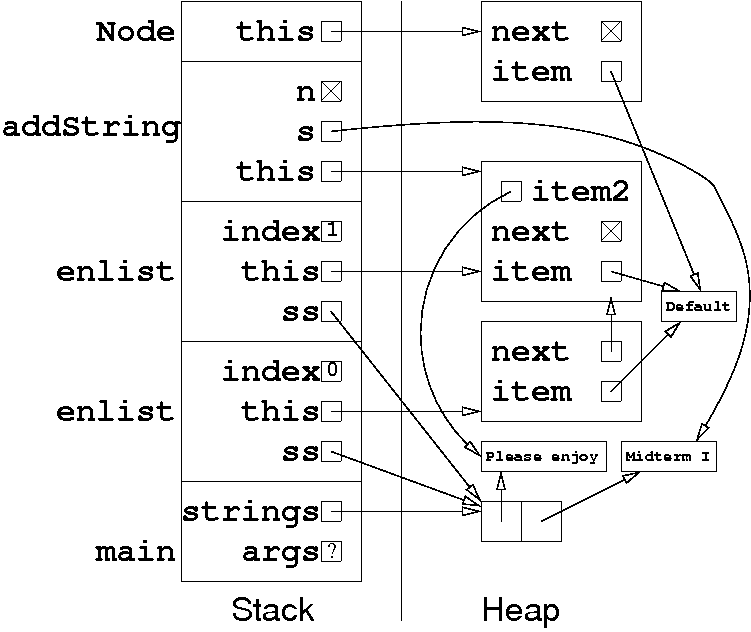
Problem 2. (9 points) The Heap and the Stack.

Problem 3. (8 points) Transposing a Matrix Represented by Linked Lists.
In this sample solution, the index j counts down rather than up, because the inner loop builds a new list from tail to head. This simplifies the code a bit.
public class SListNode {
public int item;
public SListNode next;
public SListNode[] transpose(SListNode[] mx, int columns) {
SListNode[] t = new SListNode[columns]; // Transposed matrix goes here.
for (int i = 0; i < columns; i++) {
for (int j = mx.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
SListNode n = mx[j];
mx[j] = n.next;
n.next = t[i];
t[i] = n;
}
}
return t;
}
}