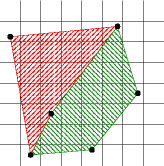
(x,y) represents the area
[x,x+1] by [y,y+1].
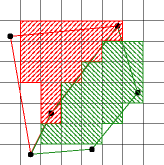
 If two polygons do not overlap, no pixel should be assigned to
both polygons.
If two polygons do not overlap, no pixel should be assigned to
both polygons.
On the right is an example of an algorithm that violates
this rule.
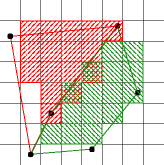
 If a set of polygons completely cover a pixel, that pixel should
be assigned to one of the polygons.
If a set of polygons completely cover a pixel, that pixel should
be assigned to one of the polygons.
On the right is an example of an algorithm that violates
this rule.

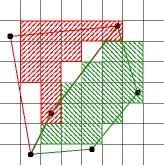
A sample point algorithm determines which polygon should contain a pixel by sampling the polygon at one point. If that one point is contained in the polygon, then the pixel is assigned to that polygon.
In this case, the sample point is the lower left corner of the
pixel. The polygon in question lies to the right of the edges
pictured The green pixel, pixel(3,7), which covers the
region [3,4]X[7,8] has sample point
(3.0,7.0). This sample point lies within the polygon,
therefore that pixel is assigned to the polygon.
The sample point (2.0,8.0) for the red pixel,
pixel(2,8), is not contained by the polygon so that pixel
is not assigned to that polygon.
When a sample point lies on an edge or vertex of a polygon, we must take care in choosing whether to assign the pixel to that polygon. Since multiple polygons can share an edge or vertex without overlapping, it is possible that we might accidentally assign that pixel to more than one of these polygons.
You can check out the results of a sample point algorithm for scan
conversion implemented in java at
http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~laura/cs184/scan/ScanTest.html
The pseudo-code for that algorithm is also available.