CS 184: COMPUTER GRAPHICS
PREVIOUS
< - - - - > CS
184 HOME < - - - - > CURRENT
< - - - - > NEXT
Lecture #26 -- We: 11/27, 2002.
Remarks about Final Project
Due
dates, deliverables.
Review of Commonly Used Spatial Subdivision and Indexing Structures:
Useful in many different contexts:
-- They can be traversed in "front-to-back" order
for ray-tracing,
-- or they can be traversed "back-to-front" for
an object-space "painter's algorithm".
-- They are also useful in collision detection,
haptics interfaces, path planning ...
-
Regular
Grid -- Simplest method; OK for scene with uniformly distributed content.
-
Octree
-- You are already familiar with this: Nice regular, adaptive "grid".
-
kD-Tree
-- A generalization: Recursively split bounding box along longest axis
near median of data.
-- A variant for indoor
scenes, floor plans: Split along major occluding walls near middle.
-
BSP
(Binary Space Partitioning) -- A generalization for scenes with big,
non-axis-aligned divider polygons.
Introduction to Color
There are many useful color spaces based on physics, the
human eye, the needs of computer graphics, the way artists'
paints
mix ...
1D space:
Artists color
wheel: "Rainbow colors": -Red-Orange-Yellow-Green-Blue-Purple-
What is red and green together ? ==> (dirty brown).
2D spaces: (more formal):
Cyan, Yellow, Magenta. ==> Subtractive mixing (filters, paint mixing).
For color printers add a good black ==> CYMK system
Computer Scientist’s wheel: 2D: Red, Green, Blue. ==> Additive mixing
(light beams, CRT).
We are missing some colors: where is brown, olive, pink, dark blue ...
?
Color space is 3-dimensional to accommodate also brightness/saturation
variations in addition to hue:
Graphics hardware view: RGB cube, store 3 intensity values for
display on CRT.
Extension of the additive color wheel to a cone (6-sided pyramid)
==> HSV.
Alternative: HLS: Double hex-cone. White/black at tips;
saturated colors on rim at height 0.5.
Physical Colors
Physicist’s View: continuous spectrum, infinite dimensions.
Typical spectrum has some broad bumps plus some sharp spectral lines
(added or subtracted).
Perceptual Colors
The human visual system has three types of cones. (Can only take 3 samples,
each over relatively broad color bands).
Sensitivity of these cones differs: green most sensitive, blue the
least.
METAMERS: colors that look the same (P), but have different spectrum(L1,
L2).
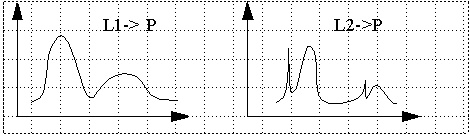
Comparative measurements are done with a color-matching set-up:

3 superposed lights (A,B,C) are compared with test color (T).
You can match almost all, but not all, colors as far as human perception
goes.
The remainder can be matched when one of the 3 colors is placed on
the test light to produce a subtractive effect.
This results in color matching functions with positive and negative
coefficients.
==> Perceptual
space is 3-dimensional. (1st Grassmann Law )
Grassman’s Laws:
(Grassman measured RGB coordinates of all perceptual colors in 5nm steps,
1931)
1. Perceptual space is 3-dimensional.
(see above)
2. Metamer mix (add) to yield metamers:
L1, L1’ -> P1; L2, L2’ -> P2; then for any a, b :
a*L1 + b*L2 -> P3; then a*L1’ + b*L2’-> P3.
(not true for paints or pigments with non-additive behavior; see example
with filter below).

3. As physical color is varied continuously, perceptual color also
varies continuously.
(continuity of the perceptual process).
Formal
perceptual color space, defined in 1931 by Commission International
de l’Eclairage (CIE).
Define a set of basis vectors that lie completely outside the range
of all visible RGB values,
so that all of the component become positive and
so that all perceptual colors map into a single octant of a rectilinear
space.
(This is a linear transformation).
Then cut this cone with the plane x+y+z=1 and project this cut onto
the x,y plane:
==> CIE
chromaticity diagram.
What can you display from this range ?
Only linear combinations of base colors. Only interpolation, i.e.,
inside the convex hull of the base colors.
==> typically a triangle ! --> Therefore, choose points as far apart
as possible.
Every output device is rather limited in the range of colors it can
display !
The typical CRT screen covers less than half of the visible domain
of colors.
(More
in next lecture ...)
Learning by Doing:
Additive
Mixing
Subtractive
Mixing
Metamers
Color
Mixing/Filtering Combination
and
many more ...
Reading Assignment:
Study: 2ndEd: Ch 7.12, 8.9.2-8.9.3,
Study: 3rdEd: Ch 8.13, 9.10.3-9.10.4,
Current Homework Assignment:
ASG#10
Final Project
CAN BE DONE WITH YOUR PARTNER OF CHOICE !
PREVIOUS
< - - - - > CS
184 HOME < - - - - > CURRENT
< - - - - > NEXT
Page Editor: Carlo H. Séquin



