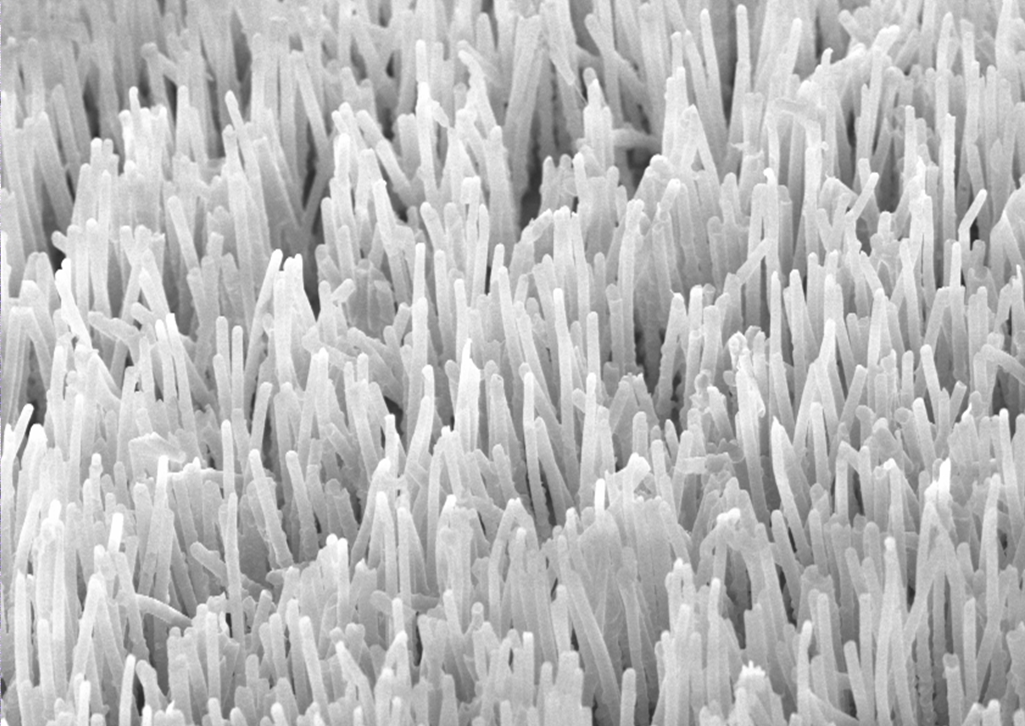
Polypropylene microfiber array
[image]
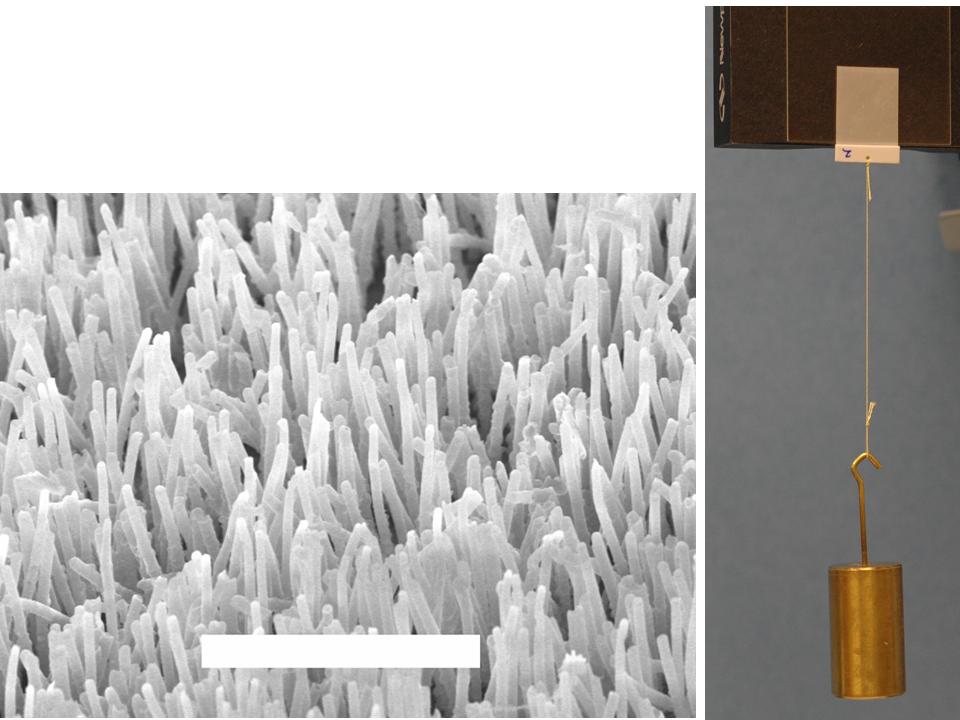
Electron microscope image of fiber array and patch holding weight
[image]
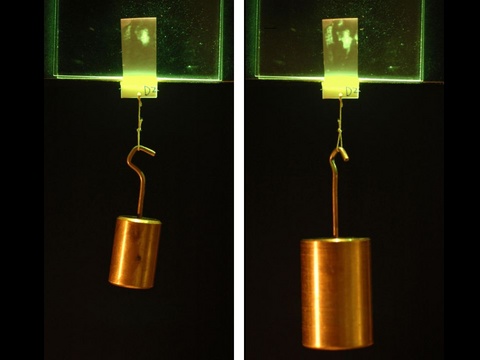
Patch supporting weight. Increasing weight increases contact area. Contact area is bright area near top of patch.
[Image]
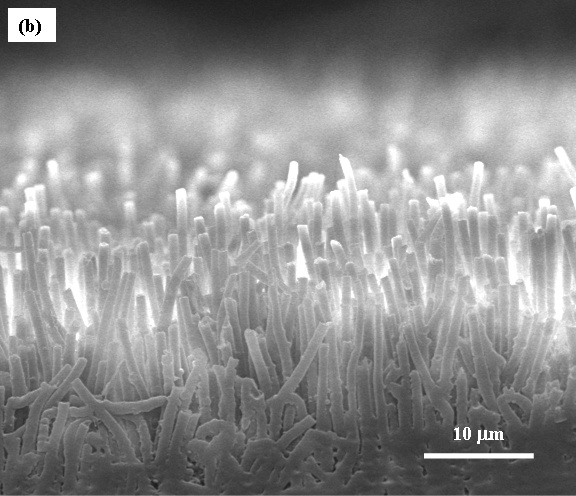
Side view of polypropylene microfiber array.
[Image]

Polypropylene synthetic gecko adhesive supporting 400 gram weight.
[Image]
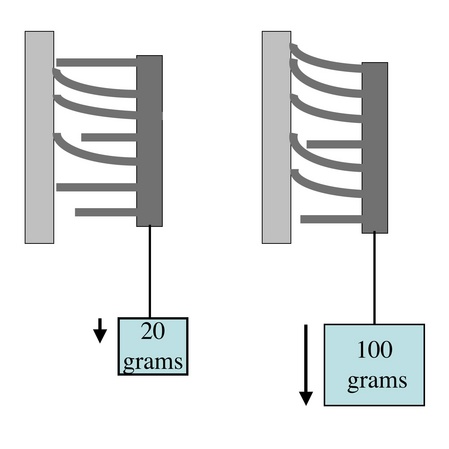
Conceptual drawing showing how more microfibers contact glass when load increases.
[Image]
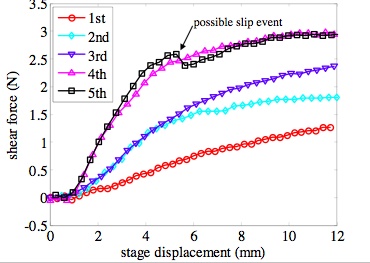
Fiber array performance improves by factor of 3 after 5 uses.
[Image]

Increase of shear adhesion with sliding distance of natural gecko.
[Image]
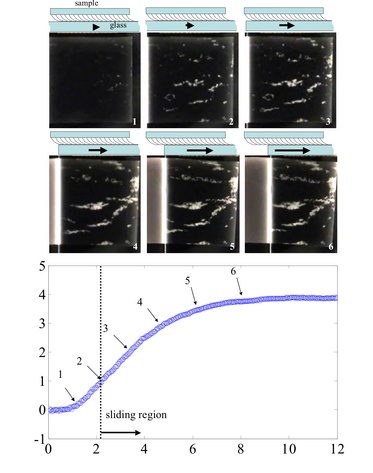
Increase of shear adhesion with sliding distance of synthetic gecko adhesive.
[Image]
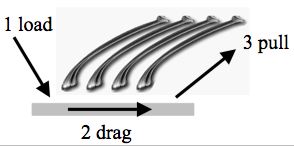
Testing path for natural gecko setal array.
[Image]
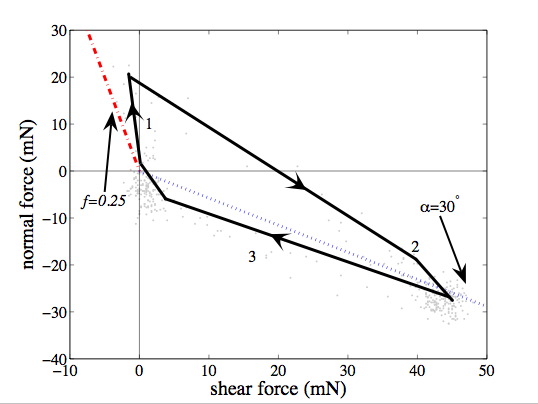
Frictional adhesion for natural gecko setal array. Normal force goes to zero when shear force is removed.
[Image]
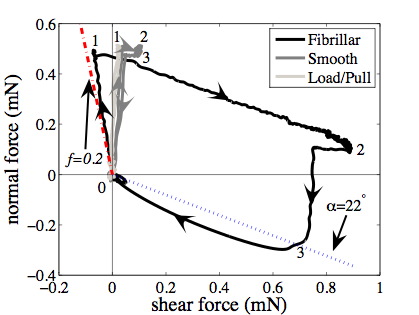
Frictional adhesion for synthetic polypropylene microfiber array. Normal force goes to zero when shear force is removed.
[Image]